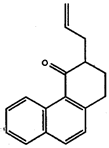
- Explain what is meant by: a) an ionic bond, b) a polar covalent bond, and c) a non-polar covalent bond. Give examples for each.
- Draw Lewis dot structures for the following formulas:
a) H3COH b) H2CO c) C02 d) C2H6 e) C2H4 f) C2H2 g) 03 h) HN03 -
Compound C-C bond length CH3-CH3 1.54 H2C=CH2 1.33 HCΞHC 1.20
a) What is the hybridization of each of the, carbons in ethane- ethylene and acetylene?
b) Why do the carbon-carbon bond lengths decrease going from ethane to ethylene to acetylene?
c) What is the hybridization of each of the carbon atoms in allene, H2C=C=CH2?
d) What would you expect for the carbon-carbon bond length of allene?
e) Draw a 3-dimensional representation of allene showing the carbon-carbon σ and π molecular orbitals.
f) Is allene a 'flat molecule' (do all the hydrogens lie in one plane)? Why or why not?
- Draw all possible line-bond structures that are consistent with the valence rules for the following molecular formula:
a) C3H7F b) C2H60 c) C2H40 d) C3H9N
- Calculate formal charges for each non-hydrogen atom in the following molecules:
a) 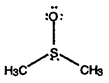
b) 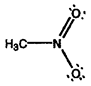
c) 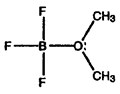
- Make 3-dimensional drawings for non-planar molecules and show the direction of the expected dipole moment for each of' these molecules:
a) H2CCl2 b) H2C=CC12 c) C12C=CC12 d) HCC13 e)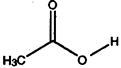
- Define Lewis acids and Lewis bases.
- Which of the following are Lewis acids and which are Lewis bases?
a) (H3C)3N: b) BF3 c) AlC13 d) (H3C)3P: e) (C2H5)2
- Convert the following structures into skeletal drawings:
a) 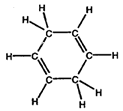
b) 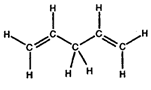
- Convert the following into Kekule structures:
a) 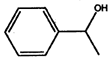
b)